What should you do if you become ill or get pregnant while working in Japan?
This chapter explains about diseases that are transmitted through sexual activity, which medical department you should go to if you become ill, and what kind of places the obstetrics/gynecology department and urology department are.
It includes information about what to do if you do not want to get pregnant in Japan, how to give birth or have a termination if you do get pregnant, and other matters related to sex that cannot be separated from our lives.
You can also read about where you can go to for advice if you have any sex-related concerns in your life in Japan and what you should do if you encounter sexual harassment or violence.

3. 1 Is it common in Japan to promise or write down that I will resign/return to my own country if I get pregnant? What will happen if I do not sign?
• That kind of promise is not permitted in Japan. Even if, either before or after you come to Japan, you are asked to promise or sign a piece of paper saying that “I will resign or return to your country if you get pregnant” or “I will return to my country if I get pregnant”, you should say, ” I do not want to sign that, I should not have to”.
• Under Japanese law, there are systems that protect pregnant women. Technical intern trainees are also protected by those systems.
• Taking time off work to attend the Obstetrics and gynecology (OB-GYN) department or if you feel unwell due to your pregnancy is permitted.
• If nothing changes even if you seek advice at your company,
you can consult your local Prefectural Labor Bureau’s
Employment Environment and Equality Department (Office).


 Comment
Comment  Did this information help?
Did this information help?[About Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)]

3. 2 My genitals are itchy, and it hurts when I pee. What should I do?
• Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are diseases that you can contract by having sex. STIs that are common among young people include HIV, HPV, herpes, chlamydia, and gonorrhea.If something feels wrong, consult a clinic or hospital near you.
• Men should go to a clinic or hospital that is listed as a urology department, STI internal medicine department or infectious disease medicine department.
• Women should go to a clinic or hospital that is listed as an OB-GYN department.




3. 3 What should I do to prevent STIs?
• You may not want to think that the person you like has a disease, but to prevent being infected or infecting a sexual partner, always use a condom when having sex.
• In addition to condoms, other ways that provide even better protection against STIs include not having sex with people other than one person you are committed to and not having direct oral sex.
• You may have been infected with an STI without your knowing.It is recommended that. Before having sex with a new partner for the first time, if you and your partner both get tested for STIs, you won’t infect the person you love without knowing it, and you can also have your own STI treated.
• Please note that the pill is for contraception, so even if you are on the pill, it will not prevent STIs.

Find out more!
Cervical cancer is a cancer affecting women that occurs around the entry to the uterus (the cervix).
It is caused by infection with a virus called human papillomavirus (HPV).
Cervical cancer is a disease that can affect any woman.
This virus is mainly transmitted by sexual intercourse.
It is a very common virus, and it is said that any woman who has had sex, even just once, has the potential to be infected.
If the cervix has been infected with the virus, it will take many years for cancer to develop.
➀The virus stays there the whole time, slowly changing into cancer, but you will not know before or immediately after the cancer is formed.
There are two ways to prevent cervical cancer.
① Get the HPV vaccine: There is a vaccine that ensures that the virus does not take up residence in the cervix.
This vaccine is given before having sexual intercourse for the first time, in other words, before the virus enters the body.
However, the vaccine cannot 100% prevent it.
Even after being vaccinated, it is important to have regular checks.
② Get regular checkups (cervical cancer screening):Even if you have had sex before having the vaccine, with regular tests and checks of the cervix, cancer or the early signs of cancer can be detected early and treated with an almost 100% success rate.
Regular checks of the cervix by a doctor is called “cervical cancer screening.”
In Japan, cervical cancer screening is conducted by your local municipal office.
It is provided for free or for a very low cost (about ¥500).
It is available for women aged 20 years and over (once every two years).


 When cervical cancer screening is conducted and how to request it is decided by your local municipal office.Ask at the municipal office, public health office, or public health center in the city, town, or village where you live.
When cervical cancer screening is conducted and how to request it is decided by your local municipal office.Ask at the municipal office, public health office, or public health center in the city, town, or village where you live. 
Find out more!

For when …
•Your genitals are stinging.
•Your genitals are swollen.
• Your genitals develop a rash.
• A pus-like mucus comes out of your genitals.
• Your underwear has unusual stains.
• You feel strange sensations (stinging, hot) when you pee.
• There is itchiness around your genitals.



For when …
or you experience severe period pain•




3. 4 I don’t want children right now. What should I do?
• If you don’t want to have children right now, you can avoid getting pregnant by using contraception.
•In Japan, there are not many contraceptive methods that can be achieved by the woman alone.The cooperation of the male partner is very important.Men should take responsibility and think about it together with their partners.
• There is no such thing as “safe days” (days when a woman will not get pregnant even if they do not use contraception). All women who menstruate have the potential to get pregnant.

|
What kinds of contraception can be used in Japan?
|
Where can I get it? | How much does it cost? |
|---|---|---|
Condoms for men |
100-yen shops, convenience stores, and drugstores. Can be bought without having to show ID, e.g. resident card.
|
Can also be bought online for ¥1,500 for a box of 100 (¥10-19 each).
|
Oral contraceptives (OC) |
OB-GYN department.Be examined by a doctor and obtain a prescription.
|
The first time will cost about ¥10,000 for the doctor’s examination, blood tests, and prescription, etc.For the second and subsequent times, it will cost about ¥2,000-3,000 for one month’s supply. Not covered by health insurance.
|
|
Intra-uterine system (IUS/IUD)
 |
OB-GYN department.The doctor will examine you and insert it on the spot. An examination is needed prior to insertion. Regular examinations will also be conducted after insertion. |
Approx. ¥40,000. Once inserted, it will continue to be effective for 3-5 years. Not covered by health insurance.
However, people with painful or heavy periods can have an IUS/IUD inserted as treatment to alleviate them.
Such cases are covered by health insurance, reducing the cost to around ¥12,000.
|
Emergency contraceptive (morning-after pill) |
Requires an examination at the OB-GYN department and a prescription.
Note: Pilot sales began at 145 pharmacies nationwide on November 28, 2023. It can be purchased without a doctor’s consultation and prescription. List of pharmacies handling the medicines Website of Japan Pharmaceutical Manufacturers’ Association Research Project for Improving the Environment for the Sale of Emergency Contraceptives *Check the four checkpoints and click on “confirm” to see the pharmacy list. |
Not covered by health insurance. |
EllaOne can be taken within 120 hours (5 days) after contraceptive failure, but has not been approved in Japan.
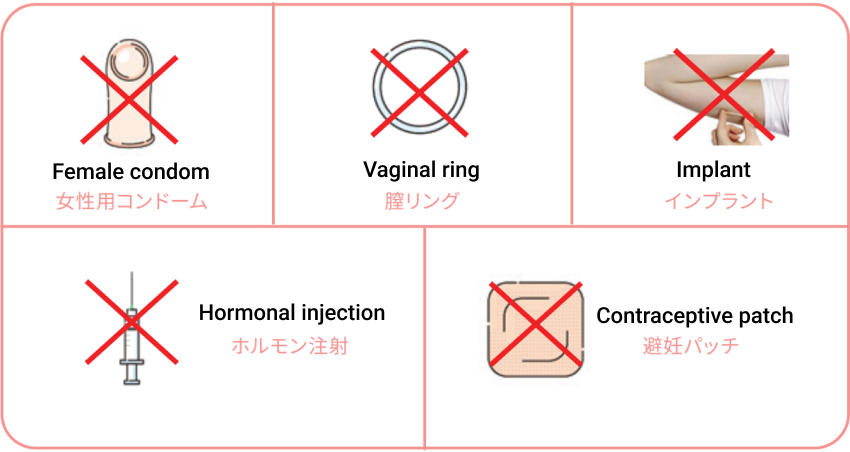
Contraceptives that are unavailable in Japan
Female condom Vaginal ring Implant Hormonal injection Contraceptive patch
Contraceptives that are unavailable in Japan
“Ninshin in Japan” website, Kumustaka – Association for Living Together with Migrants
Find out more!
Column: Bringing Medicines into Japan
•You may bring in up to one month’s supply of your own medication.
•Bringing more than one month’s supply of medicines into Japan requires Import Confirmation Certificate procedures. Submit the “Import Confirmation Form” to customs along with the doctor’s prescription or medical certificate, and the product information for the medicine. Giving or selling medicine you brought into Japan to others is illegal and considered a violation of the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act, punishable by 1 to 2 years in prison or a fine of 1 to 2 million yen.
Absolutely do not do this.
Personal importation of pharmaceuticals and other products (Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare)
https://kouseikyoku.mhlw.go.jp/kantoshinetsu/iji/yakkanhp-kaishu-2016-3.html


3. 5 I might be pregnant. What should I do?
• If you think your period is late or that you might be pregnant, take a pregnancy test or go to the OB-GYN department as soon as possible.
• In Japan, you can buy pregnancy test kits at drugstores (pharmacies) (cost: ¥500-1,000).
• Many people first buy and take a pregnancy test themselves and then go to the OB-GYN department if the test is positive.
• Usually, you will be 5-6 weeks along by the time you realize you are pregnant.
• If you want to have the baby, you will want to know as soon as possible what to be careful about during the pregnancy, and if you submit a pregnancy notification, you can receive various forms of assistance.
• If you are unable to have the baby, you can have an induced abortion before 22 weeks gestation (up to 21 weeks and 6 days).
• In Japan, women who have abortions and doctors who perform them are not punished.
• You can have an abortion safely at a designated OB-GYN department.
• If you think you might be pregnant or if you are pregnant, but you don’t know what to do, don’t worry by yourself. Seek advice immediately.

Find out more!
birth in Japan.

In Japan, there is a law that says you cannot be dismissed from your company for the reason of pregnancy or childbirth. Women who work while pregnant and after giving birth are protected by law. Foreign technical intern trainees are also protected by this law if they fall pregnant (this is written in the Technical Intern Trainee Handbook).
1) Am I covered by health insurance if I give birth in Japan?
Pregnancy and childbirth are basically not covered by health insurance, but local (municipal) governments pay a certain amount of money. Once you know you are pregnant, submit a pregnancy notification at your local municipal office as soon as possible so that you can access these payments.
2) How will pregnancy and childbirth affect visa status?
Foreign technical intern trainees who give birth in Japan or Vietnam will temporarily be suspended. However, they can return after taking maternity leave. The visa status of the technical intern trainee who is the mother can be renewed or changed.
There is also a medical care scheme for people without residence status who become pregnant.
- There is a scheme in which the local government will pay the cost of childbirth for people who are unable to afford it themselves (full or partial payment).You will apply at your local municipal office.
- You can receive a Maternal and Child Health Handbook.
- You can receive regular check-ups to check the health of the pregnant woman and the baby after it is born.
- You can be vaccinated against infectious diseases that the national government recommends that everyone needs.
You will receive the vaccines at your local municipal office.
To Japanese associates
- There is also a medical care scheme for people without residence status who become pregnant.
- Measures for admission of expectant and nursing mothers, use of in-hospital midwifery care system (Article 22 of the Child Welfare Act)
- Issuance of Maternal and Child Health Handbook, regular check-ups during pregnancy and after birth (Article 16, Maternal and Child Health Act)
- Regular immunizations (Article 5, Immunization Act)
3) What should I do if I decide to give birth in Japan?
The first thing to do is to go to your local municipal office and tell them that you are pregnant and wish to submit a pregnancy notification. They will tell you how to submit the notification. Once you have submitted the notification, you can receive a Maternal and Child Health Handbook. You can use this handbook to receive support from the municipal office’s public health nurse until you give birth.
Find out more!
4) What support or benefits are available during pregnancy, childbirth, and childcare?
Make sure to have an antenatal check-up.
If you need time off to receive a antenatal check-up, apply to the company.
(Whether it is paid or unpaid depends on company regulations.)
During pregnancy, a woman may ask her employer to allow her to avoid working overtime, working on holidays, or working late at night (Article 66 of the Labor Standards Law).
You can also ask your employer to change to lighter duties that are less physically demanding (Article 65 of the Labor Standards Law).
If you have morning sickness and are asked by your doctor to reduce your work or take time off, ask your doctor to write a “Maternal Health Management Guidance Card” and inform the company (Article 13 of the Equal Employment Opportunity Law).
You can take prenatal leave and postnatal leave.
Antenatal leave can be taken six weeks before the expected delivery date if you request it.
Employers must grant antenatal leave when requested.
Postnatal leave: No work for 8 weeks after childbirth.
Employers must not let them work.
However, you can request a return to work after 6 weeks of childbirth. (Article 65 of the Labour Standards Act)
・During antinatal and postnatal leave, approximately two-thirds of your salary is paid by health insurance as maternity allowance.
If you continue to receive your full falary from you company during your leave, you will not be eligible for the maternity allowance if the salary exceeds the amount of the allowance.
Money you can receive after giving birth:
If you are enrolled in health insurance, you can receive 420,000 yen per child as a “childbirth and childcare lump-sum payment” after giving birth.
However, since you may need to pay the childbirth expenses upfront, please consult with the medical institution.
Anyone raising a child under the age of one, regardless of gender, can take time off to care for their child (parental leave system).
There is financial support available for those who take parental leave to care for a child under the age of one (“Parental Leave Benefit”).
Employers are prohibited from dismissing, making unfavorable transfers, or reducing wages due to reasons such as pregnancy, childbirth, maternity and paternity leave, or parental leave (Article 9, Section 3 of the Equal Employment Opportunity Law, Article 10 of the Child Care and Family Care Leave Law, etc.).
If you are in trouble, find a nearby consultation center from the website below to seek advice.
Comprehensive consultation service for foreign workers (14 languages)
Minstry of Health, Labour and Welfare 
5) What should I do if I decide to return to my country to give birth?
Technical intern trainees who wish to return to their own country to give birth must first ask their supervising organization to undertake the necessary procedures at the Organization for Technical Intern Training.To resume technical intern training, after having a new technical intern training plan approved by the Organization for Technical Intern Training, they can apply with the Immigration Bureau and return to Japan on a Technical Intern Trainee visa.
• Information page about pregnancy in Japan – Association of Living with Foreigners
6) What should I do if I decide not to have the baby?
•Under Japanese law, you can have an induced abortion before 22 weeks gestation (up to 21 weeks and 6 days).
• The method of abortion varies depending on the gestational age.
In Japan, early-stage abortions (before 12 weeks) are typically performed on an outpatient basis or with an overnight stay.
In the case of a mid-term abortion (between 12 and 22 weeks), the patient typically stays in the hospital for several days to about a week.
• The abortion operation performed differs between early pregnancy (less than 12 weeks) and later, and the impact on the woman’s body also differs.
If you decide to have an abortion, doing so early will place less burden on your body.
The oral abortion pill was approved in Japan in April 2023, but it is not available for purchase at pharmacies.
Search for hospitals and clinics where you can consult about abortion pills
About abortion pill 「MEFEEGO Pack 」Minstry of Health, Labour and Welfare
• The oral abortion medication Mefeego Pack can be used up to 9 weeks of pregnancy.
• Abortion operations are not covered by health insurance.
Although it varies at different clinics and hospitals, an abortion in the early stage of pregnancy costs around ¥100,000.
• If you are in the middle stage of pregnancy and require hospitalization, you should also check with the hospital about admission charges beforehand.
• In Japan, when using the oral abortion pill, an overnight hospitalization is required, so please check with the hospital in advance regarding the hospitalization fees.
After an abortion, you may experience physical and mental changes.
* Physical … After an abortion, bleeding may be prolonged, and your next period may come early or be late.
* Mental … You may feel depressed for a long time due to feelings of guilt.
• There also some women who become unable to trust their partner between finding out they are pregnant and deciding to have an abortion.
• These kinds of changes are not unusual.
• If you are worried, don’t delay in consulting the OB-GYN department or a place that provides mental health consultations.
Under Japanese law, only designated doctors are authorized to prescribe the oral abortion pill or perform the procedure.
Having abortion drugs sent to you from your own country or bringing them in yourself and taking them in Japan is punishable by Japanese law.
• Moreover, it is dangerous to abort a pregnancy with drugs without being examined by a doctor.
If you have concerns, seek advice immediately.
Message to Men
If, after discussing it with your partner, you both choose to have an abortion, support your partner and get through it together.
7) It is too late for me to have an abortion, so I have no choice but to give birth.
If you give birth alone without having seen a doctor and the baby dies, you may be subject to punishment under Japanese law. No matter what your situation, once you know you are pregnant, consult a doctor.
8) More information and consultation services
Ninshin in Japan
Kumustaka – Association for Living Together with Migrants (5 langugages) 
・Who can I consult about pregnancy in Kumamoto?
・I don’t want to have children now. What should I do?
・I may be pregnant. What should I do?
・I want to have a baby. Do I have to quit my job or school?
・How much does it cost to have a baby in Japan?
・How will the status of residence be when I become pregnant or give birth in Japan?
・I don’t have a visa. I’m pregnant. What should I do?
・What should I do to have a baby in Japan?
・What should I do when I want to return to my country and give birth?
・What should I do if I don’t want to have a baby?
・What should I do if I give birth but cannot raise the child?
・The story of those who gave birth in Japan
Mother and Baby Support Series (20 langugaes)
Parenting in Japan -From pregnancy to enrolling in elementary school-Kanagawa International Foundation (11 langugaes)
Seek advice

3. 6 I have been a victim of a sex crime (rape). What should I do?
• Rape and molestation are sex crimes under Japanese law.
• You can decide when, where, who with, and what kind of sexual relations you have.
• Sexual acts that you do not want, especially in situations where it’s hard to say “no,” are considered sexual violence.
(These are referred to as the crimes of non-consensual sexual intercourse and non-consensual indecent acts.)
• Sexual violence occurs regardless of age or gender.
• In any situation, it is not your fault if you have been harmed.
• It also occurs between people we know and between married couples or partners (See 3.7).
• Sex crimes and sexual violence are absolutely unacceptable.
• If you are distressed or anxious, do not suffer alone, and instead, seek advice.

[Detailed Information in Japanese]

• This is a consultation service for sexual crimes and sexual violence.
• Nationwide toll-free number #8891 (available 24 hours a day)
• This will connect you to the nearest One-Stop Support Center for victims of sexual assault and sexual violence.
• List of one-stop support centers for victims of sex crimes and sexual violence
• This is a list of hotlines around Japan that provide consultations regarding sex crimes and sexual violence.
• They also coordinate with OB-GYN care, counselling, and legal advice services.
• Hotline for Male Victims of Sexual Violence (All counselors are male)
0120-213-533(Toll-free number)
• Every satuday from 19:00 to 21:00.

3. 7 My partner is violent toward me, and I am suffering. What should I do?
• Domestic violence* (DV: violence committed by a current or former partner) is a crime and absolutely unacceptable.
• In Japan, the DV Prevention Act** protects people who have been subjected to violence by their partners. This law also applies to all foreign nationals in Japan.
•This is often difficult to resolve on your own, so seek advice.
*Domestic Violence (DV): Bạo lực gia đình
**DV Prevention Act: Act on the Prevention of Spousal Violence and the Protection of Victims

Seek Advice in English
* National Policy Agency website (npa.go.jp)
[Detailed Information in Japanese] Reference information: For Japanese associates

[Detailed Information in Japanese] Reference information: For Japanese associates
“What is Domestic Violence (DV)? Gender Equality Bureau Cabinet Office (Japanese)”
Victims of DV are protected, regardless of residence status (Immigration Services Agency Notification No. 26)